7 Chenzhou Cultural Protection Units Newly Promoted as "National Key Cultural Relics Protection Units"
Recently, the official website of the Central People's Government released the "Notice of the State Council on the Approval and Promulgation of the Eighth Batch of National Key Cultural Relics Protection Units". 7 cultural protection units in Chenzhou City were selected, including the site of the Dutou ancient city during the Han Dynasty to the Six Dynasties in Linwu County and the site of Tongmuling Mining and Smelting in the Qing Dynasty in Guiyang County.
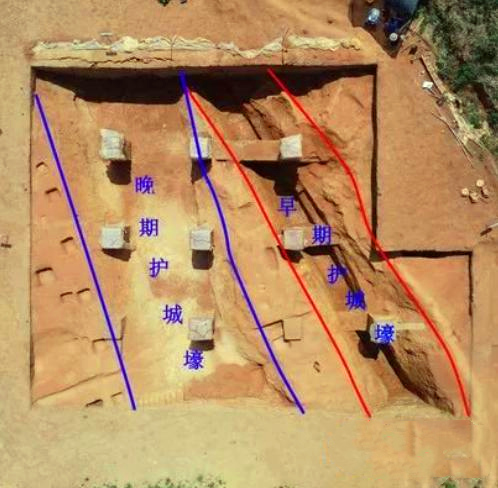
Located in the south bank of Wushui River, Dutou Village, Fenshi Town, Linwu County, Chenzhou City, Dutou ancient city site is about 13 kilometers away from the county in the southwest and is an ancient city settlement site centered on the site of Dutou ancient city and including the surrounding tombs.
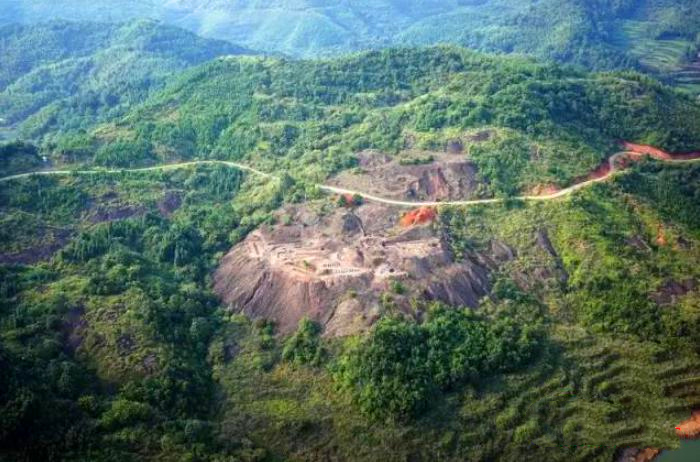

Panoramic View of Tongmuling Site (from South to North)
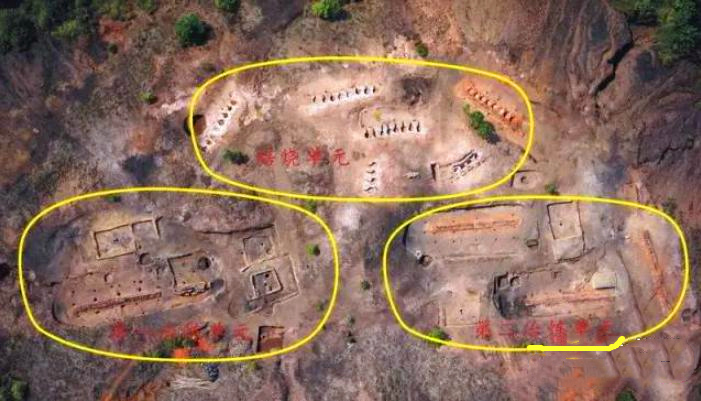

Functional Zone Map of Tongmuling Site (from North to South)
Tongmuling Site unearthed the most complete ancient zinc smelting trough furnace and related relics in China, which can fully recover the zinc smelting process at that time. The discovered zinc sulfide ore roasting furnace and roasting process are a major technological progress in the ancient history of zinc smelting in China. There are also smelting activities of lead, silver, copper and other metals in the site, and the integrated smelting of multi metals is the research of China's mining and metallurgy. The first discovery in ancient times indicates that the comprehensive utilization of ore has been further improved, highlighting the advanced level of science and technology in ancient China.
Tongmuling mining and smelting site was excavated by Hunan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, Archaeology and Museology School of Peking University, and Guiyang County Cultural Relics Management Institute, which was awarded the "Top 10 National Archaeological Discoveries in 2016".




